Energy Efficiency
Your Clear Choice for
Energy Efficiency
No matter the climate, or the local building codes, or home style, you can be sure that Marvin has the products and options you need to conserve energy and bring efficiency to your whole-house system.
Our windows and doors have always featured the materials, designs, and options to meet a full range of climate and code requirements. Contact your dealer or builder to learn more.
Energy Efficiency Basics
What’s the first thing I need to know when it comes to windows and energy efficiency?
Replacing older windows with more energy-efficient units can help reduce your utility bills, but it can also make your home more comfortable. Choosing the right windows and doors can help you regulate how much heat comes into and escapes from your home.
How do I know if a window or a door is energy efficient?
Certification programs such as those administered by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) and ENERGY STAR provide ratings designed to indicate a window or door’s efficiency. Various performance ratings – like U-factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient – measure a product’s effectiveness in insulating and blocking heat from the sun, among other things. See the Glossary of Terms.
Are energy efficient windows and doors tax deductible?
Tax credit programs change often. To stay up-to-date with the latest federal, state, and local energy provider offers and rebates, visit www.energystar.gov/about/federal_tax_credits or read the Marvin Manufacturers' Certification Statement.
Terms You Should Know
Across products and manufacturers, these are some common terms used to describe the energy efficiency of windows and doors.
Insulating Glass (IG)
Two or more glass panes separated by energy efficient inert gas or air to reduce thermal transfer.
Gas Fills
Argon or krypton mixes slow the movement of warm and cool air in IG airspaces and improve thermal performance.
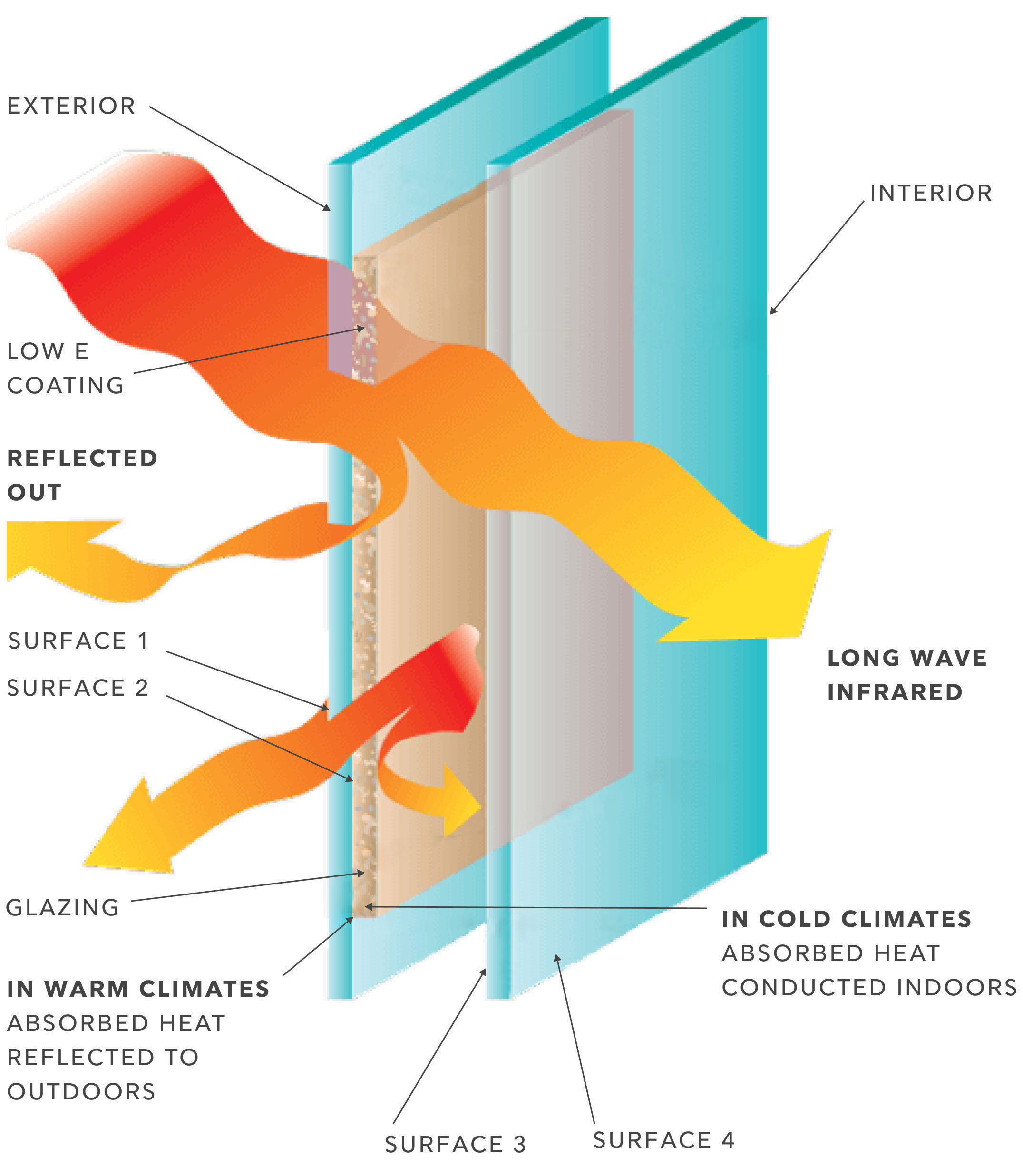
Low E
Low E stands for low emissivity. Microscopically thin, transparent metal or metallic oxide layers deposited on a glass surface suppress radiative heat flow and reflect interior infrared energy (heat) back to the inside, reducing heat loss through the glass. Various Low E coating options can manipulate heat gain to match different climate needs.
Visible Transmittance
Visible transmittance is the amount of visible light transferred through a window. Low E coatings can reject solar heat gain without significant reduction to visible light passing through the glass. When you look at the ratings, remember that the higher the number given for visible transmittance, the more light that can come in.
U-Factor
Simply put, U-factor measures how well a window keeps heat inside your home. It’s a measure of total heat flow through a window or door from room air to outside air. Lower numbers indicate greater insulating capabilities. It’s a particularly important measure for climates with colder winters.
Solar Heat Gain
If U-factor denotes how much heat leaves your home, the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) measures how much radiant heat enters your home. All you really need to know is: The lower the number, the less heat a window lets in.
What does it mean to be an ENERGY STAR-certified window or door?
Though not generally a requirement like local, state, and federal building codes, ENERGY STAR certification is a set of standards established to meet what the U.S. government considers an efficient window or door. Those requirements differ based on geography, meaning a window that’s being installed in Minnesota has different requirements than one in Florida. The certification is meant to indicate that the window is energy efficient in the region where it will be used and can help homeowners save on energy costs but is not a factor when it comes to passing inspections. Contact a local building official or certified building professional for more details.
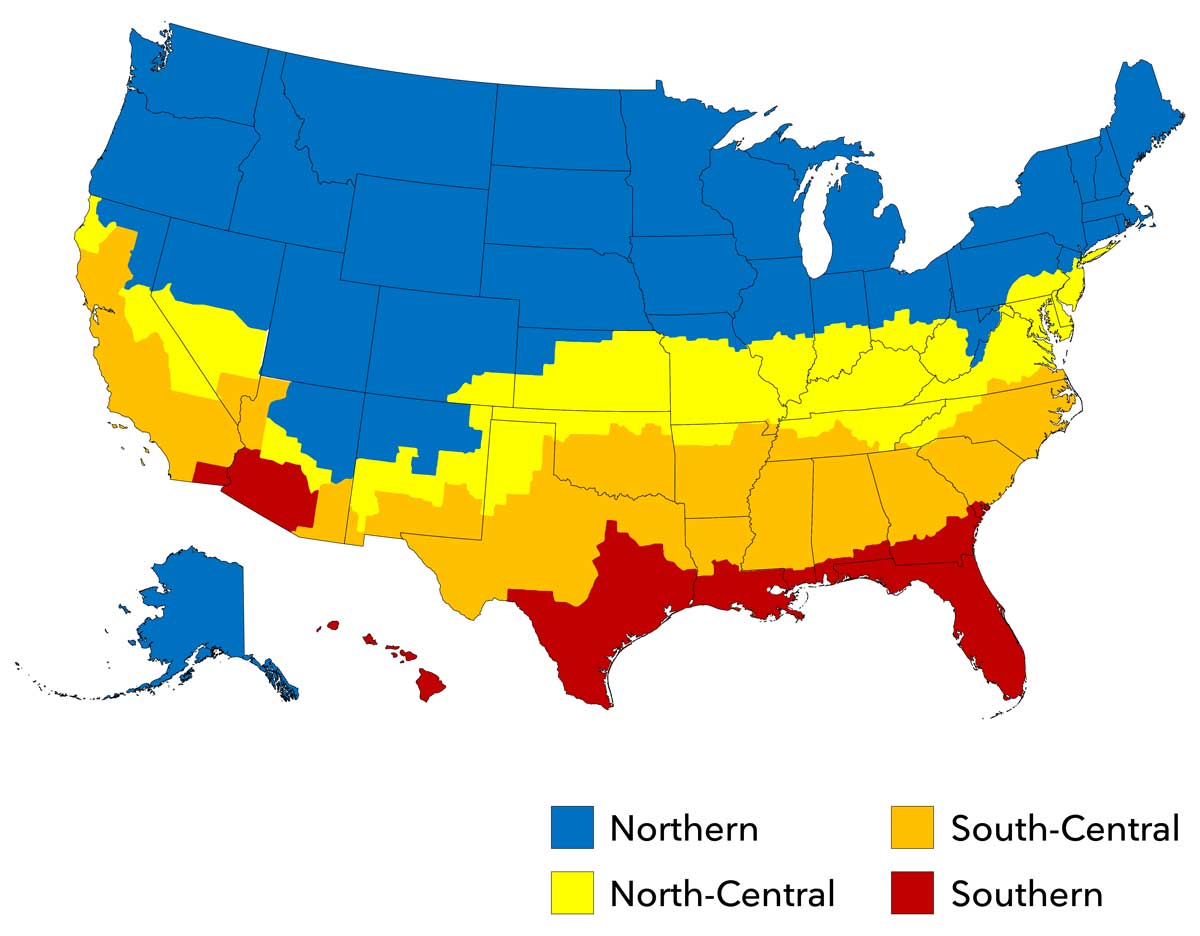
ENERGY STAR Criteria
| Zone | Window U-Factor | Window SHGC | Door U-Factor | Door SHGC | Skylight U-Factor | Skylight SHGC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern | ≤ 0.22 = 0.23* = 0.24* = 0.25* = 0.26* |
≥ 0.17 ≥ 0.35* ≥ 0.35* ≥ 0.40* ≥ 0.40* |
≤ 0.26 | ≤ 0.40 | ≤ 0.45 | Any |
| North Central | ≤ 0.25 | ≤ 0.40 | ≤ 0.26 | ≤ 0.40 | ≤ 0.50 | ≤ 0.25 |
| South Central | ≤ 0.28 | ≤ 0.23 | ≤ 0.28 | ≤ 0.23 | ≤ 0.50 | ≤ 0.25 |
| Southern | ≤ 0.32 | ≤ 0.23 | ≤ 0.28 | ≤ 0.23 | ≤ 0.50 | ≤ 0.25 |
*Equivalent Energy Performance
Does my window need to be ENERGY STAR certified in order to be energy efficient?
No. While an ENERGY STAR label can be helpful in identifying energy-efficient windows, every home is unique. ENERGY STAR provides a one-size-fits-all guideline but does not take into consideration, for example, the orientation of the house or the number or size of windows and associated Solar Heat Gain. A window expert like your Marvin dealer can help determine which products will work best for you. Marvin offers a wide selection of products that meet these rigorous criteria. Learn more at the EPA ENERGY STAR website.
| Glazing | Description | Climate | Energy Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low E1 | Features a single layer of metallic coating, which blocks heat loss to the outside while reflecting heat back into the room. | Northern | Low U-Factor High solar heat gain |
| Low E2 | Features a double layer of silver on an inside surface of IG glass. It provides year round performance and comfort. This coating option provides better protection against radiant heat transfer than single layer metallic Low E coatings. | Northern North-Central South-Central |
Low U-Factor Medium Solar Heat Gain |
| Low E3 | Features three layers of metallic silver and provides the lowest solar heat gain performance in climates where sun exposure is intense and cooling costs are high. | Northern North-Central South-Central Southern |
Lower U-Factor Lower Solar Heat Gain |
| Low ERS | A high performance insulating glass that features an additional Low-E coating on the room-side glass surface. | Northern North-Central South-Central Southern |
Lowest U-Factor |
Can you help me to better understand the numbers? What’s a good U-factor number? What’s a good SHGC?
Different homeowners seek out different levels of efficiency, but a “good” U-factor is <.30. In the Northern Zones, a U-Factor even lower than .30 may be beneficial to increase your energy efficiency and home comfort. A “good” Solar Heat Gain rating, meanwhile, on a scale from 0 to 1, is relative to climates in different regions. Low SHGC numbers are best for southern climates where there’s intense sun exposure, whereas higher SHGC values may make sense for regions with cold winters.
What are Low E Coatings?
The ability of a material to radiate energy (heat) is called its emissivity. Extremely thin coatings of special low emissivity (Low E) metallic material are applied to glass panes used in windows and doors to boost their energy efficiency. Low E coatings, usually applied to the inside layers of insulating glass, manage the amount of light and heat either transmitted through a window or reflected away from it.
What are the advantages to selecting triple pane windows?
Triple pane windows work best when enhanced energy performance is a key objective. Triple pane windows are designed to reduce U-Factor as compared to dual pane. They offer a range of low-E window configurations, along with Low ERS, and with either an argon gas fill or air for high altitude applications. Triple pane glass can also provide more in home comfort in cold environments because the interior surface of the glass is warmer, reducing convection currents. But no matter how many panes there are, if the window is poorly constructed, poorly installed, or allows air leakage, it will be inefficient.

High Performance
Energy efficiency is achieved through the use of various window and door technologies. Low E coatings, frame materials, glazing types, spacers, gas fill, and weather stripping all contribute to efficiency. Energy ratings for windows and doors are certified by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC). Browse the NFRC database to see their ratings for any Marvin product.
What else do I need to know if I want to make my home super energy efficient?
It’s easier than ever before. Modern sustainable building methods, like Passive building, LEED® (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and Net Zero building can help you minimize environmental impact and maximize energy efficiency. ENERGY STAR also offers a “Most Efficient” list, a distinction that recognizes products that deliver superior efficiency through cutting-edge technologies and innovations. Marvin has the options you need to meet your energy efficiency goals. Reach out to your local dealer or Marvin representative to find out more. Learn more about most efficient products at the EPA ENERGY STAR website.
Is sustainable building the same as high performance building?
Sustainable building refers to both a structure and to processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building’s life-cycle: from siting to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. According to the National Institute of Building Sciences, high performance building integrates and optimizes all major high-performing building attributes, including energy efficiency, durability, lifecycle performance, and occupant productivity.
Can I make my home a high performance building?
There are methods to optimize energy efficiency in a home environment, most easily with new construction. One way is to plan for a building to generate at least as much energy as it consumes. Net Zero homes and Zero Net Ready homes are carefully designed structures that currently or in the future make use of alternative energy solutions such as wind, solar and/or geothermal systems. You don’t need to build a Net Zero home to dramatically improve energy performance in your home. Whether replacing windows in an existing home or designing for new construction, there are plenty of energy-saving windows to choose from.
Find a Dealer
Marvin experts are experienced in working with architects, builders, and homeowners to ensure your vision becomes a reality.